The world of technology is fast-paced and has seen its share of trends. Cloud computing has got to the point where almost everybody has used a cloud service at least once, and some rely on such services to keep a business running. But is cloud computing a good career?
Cloud computing is a good career, as the industry is one of the most exciting areas of technology today. The demand for creative and innovative engineers to get the best cloud computing platform means salaries are high, and the future longevity of the sector is very healthy.
I’ll take you through how we got to the current state of cloud computing, as well as some figures to show the current size and potential future growth. We’ll also look at some cloud computing roles and their salaries to see what opportunities exist to make cloud computing a career.
The Current State of Cloud Computing
The IDC states growth in the cloud computing sector has been steady for several years. The United States currently boasts a huge cloud computing landscape, with North America commanding a 70.52% share of the global market already in 2022. This dominance is fueled by the presence of major cloud providers such as Amazon, IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, and Oracle Corporation.
These companies are actively investing in technical expertise, partnerships, and the expansion of cloud centers. Cloud adoption has seen a rise across various sectors in the U.S., including IT and telecommunications, healthcare, consumer goods and retail, and manufacturing.
Additionally, the U.S. and Western Europe remain at the forefront of cloud computing, jointly representing 82% of the global market. In the U.S., over 94% of enterprise organizations have embraced cloud solutions, with many exploring multi-cloud or hybrid cloud approaches. A significant portion of U.S. organizations have adopted a cloud-first strategy for deploying new applications, and a substantial percentage plan to migrate their workloads to the public cloud.
Several factors have caused cloud computing to become so important.
At its most basic level, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet. This may include, but is not limited to:
- Storage
- Databases
- Servers
- Networking solutions
- Virtual machines
- Software packages
- Analytics
- Artificial intelligence
The key is that you are only paying for those specific services you use and not on the hook for the complete development or maintenance of the infrastructure. Fundamentally, this means that an organization can both lower operating costs, get more efficiency from existing systems, and have instant scalability as required.
Analysis shows that the cloud computing market size globally was 274.79 billion in 2020. On top of this, cloud computing is projected to have an annual growth rate of 19.1% through 2028.
Factors Behind Cloud Computing’s Rise
There is a considerable increase in digitization and the growth in moving to flexible workplaces, which means that data needs to be stored and readily accessed.
Organizations that don’t modernize their internal processes to reap the benefits of cloud computing will have difficulty competing with firms that do. Not only does a move to cloud computing drive cost efficiency, but it also reveals business agility.
The on-demand nature of services like storage, software, and remote processing over the internet has seen a meteoric rise in cloud computing. Notably, cloud computing is run as a service that eliminates the need for some local IT specialists to manage cloud services actively.
The demands of keeping a cloud system or proprietary software working are complex and out of the range of most IT professionals.
The shift of technology usage has shifted, sometimes referred to as the consumerization of IT.
This means that rather than technology starting at the business level and then appearing in the consumer market, now the technology adoption and usage proficiency among employees sees these technologies getting pushed into the workplace.
Cloud computing has also been able to sell itself to an extent.
The awareness of the benefits of cloud computing through high-profile rollouts like Google’s suite, as well as a ballooning startup environment, sees entrepreneurs vying for new ways to sell novel cloud-based solutions.
Image from Microsoft
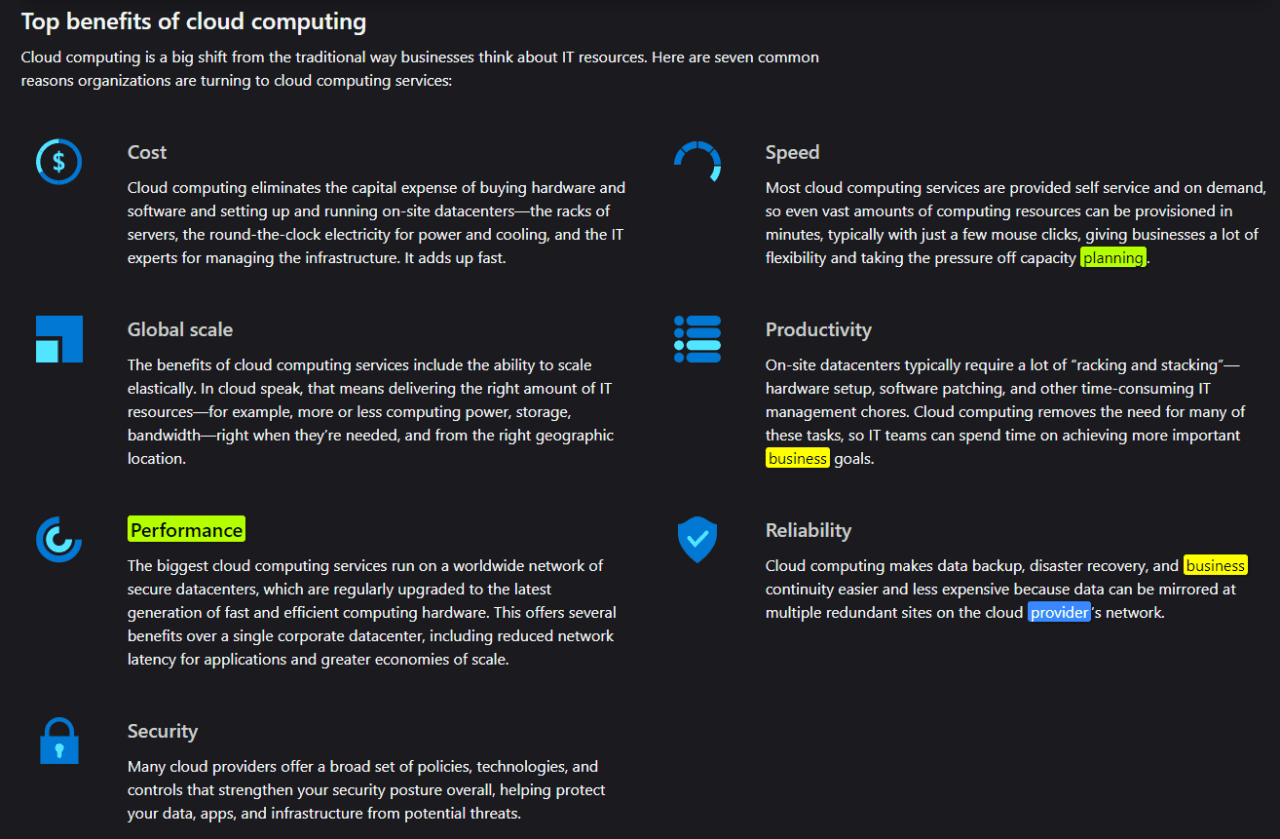
In the end, cloud computing offers solutions and covers some critical areas. Security concerns regarding encryption, access control, communication vulnerabilities, backups, and monitoring are handled well via cloud computing.
On top of this, the service reliability from top-level cloud computing providers is hard to match with a local solution. With the massive range of server farms, engineers, backups, and other systems, such vendors can offer 99.9% uptime.
Not only does this allow for businesses to operate without interruption, but it also relieves them from the burden of creating and maintaining in-house systems.
What Does the Future Hold for Cloud Computing?
The global cloud computing market is projected to achieve substantial growth, with estimates suggesting it could reach USD 1,266.4 billion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.1%. Another forecast anticipates the market to expand from $677.95 billion in 2023 to $2,432.87 billion by 2030, demonstrating a CAGR of 20.0% during the forecast period. Moreover, the market size was valued at USD 483.98 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to register a CAGR of 14.1% from 2023 to 2030. These projections indicate a significant and rapid evolution of the global cloud computing market in the coming years.
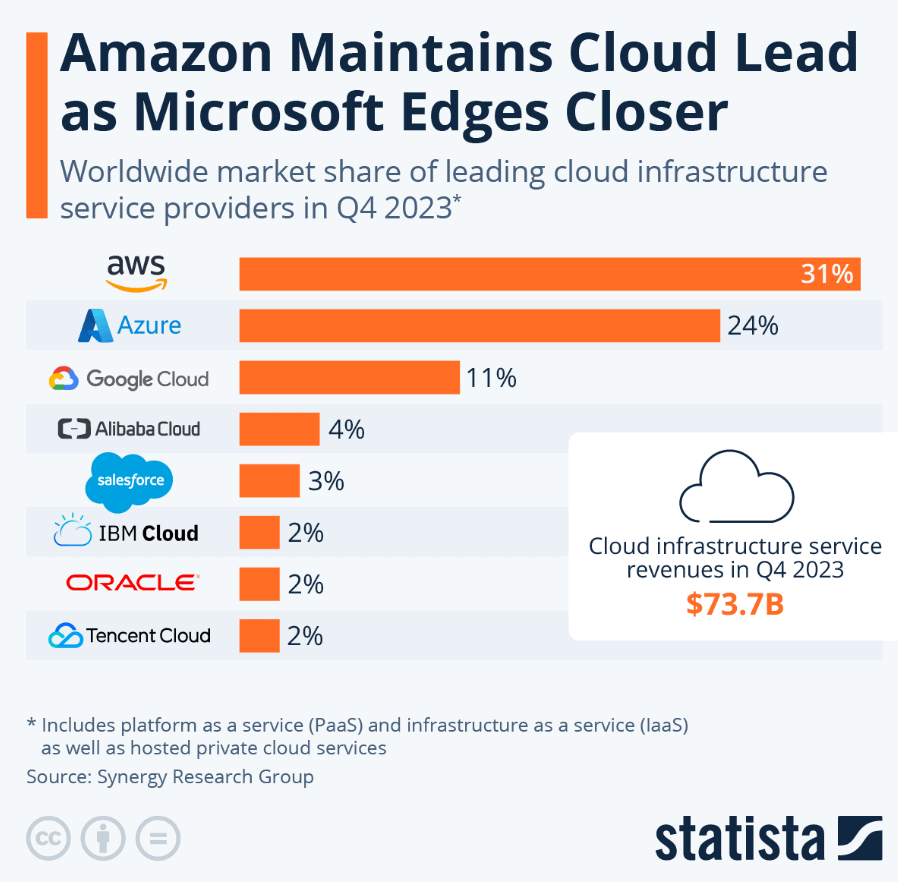
The most significant player in the market is by far Amazon Web Services (AWS). Amazon Web Services in 2020 was 32% of the total market down to 31%. In recent years, Google has joined the race at 11% and, after some adjustments, is becoming more prominent in the space.
Google increased its workforce to 37,000 for its cloud services while other departments are downsizing. Their earnings reports reveal that the cloud department’s revenue grew over expectations for the past few years.
The Largest Segment Who Uses Cloud Computing
The segment to dominate the usage of cloud services is the banking, financial services, and insurance sector (BFSI), which had the highest market share of over 25% in 2020.
Cloud computing offers everything that banking customers and firms want. Secure storage and the ability to have constant uptime have helped the BFSI move towards a better customer-centric business model and ongoing complete digitalization of money management.
However, it is not just the service or financial industry which is benefiting from cloud computing. The manufacturing industry is ideally suited to cloud services, like data management, real-time analysis, and organizational-wide visibility.
Other Major Segments
One of the most significant growth areas in cloud computing is Software as a Service (SaaS), which is a way to provide software access over the internet. The cloud provider runs the software on their servers, usually located remotely in a data center.
SaaS accounted for 54% of the cloud revenue back in 2020, which resulted from a flurry of acquisitions in 2018 when 169 companies were acquired by the various players in the cloud market.
The dominance of cloud computing is also evident by measuring workload processing. Cisco Systems revealed that more than 94% of the workloads would be processed by cloud data centers in 2021. For reference, the figures for 2019 were 60% and 45% in 2018.
Why Cloud Computing Shines
Crunching data is often where cloud computing shines.
Getting real-time visibility on consumer habits and then suggesting or offering solutions will revolutionize many more sectors than just banking or manufacturing.
Healthcare is prime for a shakeup by better leveraging cloud computing.
Instant sharing of data, wearable health devices collecting the data, and automated check-ins mean consumers can achieve better health outcomes by integrating more in-depth data analysis.
Interestingly, it is not just these massive tech giants pushing innovation in the cloud sphere. The rise in cloud-based deployment for product offerings by small and big firms alike is driving the market growth.
This implementation of cloud computing is beneficial for cross-compatibility.
One prime instance is the introduction in 2018 was Adobe’s Experience Cloud Device Co-op. Cloud computing then enables service rollout for all end-users, no matter their device, with no degradation of consumer experience.
The Future Of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing is forecasted to continue at over 10% growth per annum up to 2025. From the demand side, the average organization’s cloud budget is seeing a double-digit increase with close to a third of company IT budgets specifically for cloud services.
Geographically, big firms in the United States have shown that they can adopt new technology quickly, which has proven to be a quick path to efficiency and flexibility in offerings. However, the Asia Pacific region is anticipated to emerge as the fastest-growing region over the next five to 10 years.
The world revenue forecast in 2028 is set to reach USD 1,251.09 billion.
Where Are the Major Employment Locations?
Currently, the three major players in cloud computing are Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS. Between them, the three make close to 60% of the total market share.
While working for these firms is guaranteed to give you a higher income, it is not the only option for working with cloud technologies.
SaaS or other cloud offerings are primarily public. This refers to the servers, equipment, engineers, and other components shared over the service.
However, it is also possible to engage in the private deployment of cloud solutions.
Indeed, the private deployment of cloud services accounted for the most significant market share, topping over 45% back in 2020.
The cost involved with setting up private infrastructure may put it out of reach of smaller organizations. Still, the benefits seen through security, data integrity, and other reasons mean it is very popular with larger firms.
Private deployment may even be a necessity due to specific regulations.
This segmentation of the cloud computing market only opens up more opportunities for careers, which is particularly apparent through the growing focus on hybrid cloud models requiring specialists who can both design and manage such solutions.
What’s Cloud Engineering?
Cloud Engineering is the practice of designing, building, operating, managing, and optimizing applications in the cloud. The cloud allows for elasticity and scalability along with lower costs and increased flexibility. This technology has become increasingly popular due to the popularity of mobile computing and the growth of big data. In addition, it provides a platform that can be accessed from anywhere at any time.
What is a Cloud Engineer?
A Cloud Engineer is responsible for designing, developing, testing, deploying, managing, monitoring, and optimizing applications running in the public, private, or hybrid clouds. They also work closely with other teams such as developers, operations engineers, etc.
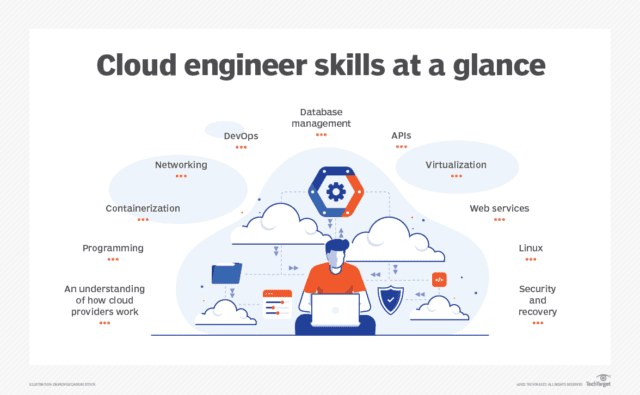
Basic skills to be a successful cloud engineer:
- Cloud computing – Experience using remote services via the web instead of local servers. These services allow users to access applications and data at any time from anywhere like AWS or Azure.
- Virtualization – Ability to use virtual machines (VMs) that simulates the hardware components of a physical server. VMs can run their own operating system or share the same host OS as other VMs.
- Storage – Ability to store information on a computer’s hard drive, flash memory, or another storage device along with some database skills.
- Networking – Understanding the communication between computers over wired or wireless networks which consist of nodes connected together, each node having its own IP address.
- Security – Know how to protect data and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, etc.
- Programming languages – There are many different programming languages, some of them being C++, Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, Perl, JavaScript, SQL, etc. which are common in cloud engineering roles
- Containerization – Ability to pack software into containers for deployment. This approach allows developers to create self-contained applications with their own dependencies.
Cloud Engineering Skills
How Do I Get a Job as a Cloud Computing Engineer?
Cloud Engineers should have at least 3 years of experience to get a job, specifically with cloud technology. Make your application stand out by showing familiarity with the primary integration points to the cloud, such as application programming interfaces (APIs) and database management.
A job in cloud computing involves managing the cloud environment from conception to delivery. The various life cycles of a cloud solution mean you have specialist designers, cloud architects, cloud security experts, and cloud maintenance.
Cloud Infrastructure Engineers specialize in cloud technology and work to optimize how the cloud overall operates. Infrastructure Engineers are vital in controlling costs and ensuring that the system works with as little wasted server power as possible.
The salary range for an Infrastructure Engineer runs from about $101,000 to $123,000.
One of the top roles to aspire to in the world of cloud computing is the Cloud Architect. Generally reserved for those with several years of expertise, Cloud Architects have a significant role in pre-migration or implementing an organizational cloud strategy.
This senior role requires formulating the entire life cycle of the cloud technology integration into a use case and forms the basis upon which Cloud Engineers and other administrators will follow the broader ICT strategy.
Given the necessary experience and scale of a Cloud Engineer’s work, the salary range is large. Anonymous salary surveys show that a national starting salary is around $130,000 but can quickly push over the $200,000 mark on large projects.
Broad experience as an app developer or network technician can give you the skills necessary to become a Cloud Developer. This position will generally require two to three years of experience in a cloud environment.
However, the starting salary is still excellent, with higher ranges going up to $180,000 and $104,000 listed as a 25th percentile boundary salary.
One of the most significant growth areas in cloud computing is security. Surveys reveal that 77% of organizations globally have planned to add encryption and heightened security to their cloud solutions.
Furthermore, 91% also believe that security will continue to gain in importance.
A Cloud Security Manager is at the forefront of implementing such solutions. Current salaries are sitting at an average of $102,000 according to Salary.com.
Best Qualifications for Cloud Computing Engineers
The major cloud platform providers offer certifications for their products, which forms the basis of most successful applications.
Amazon offers a variety of cloud computing certifications to reach a higher level of qualifications. These include:
- AWS Certified Developer
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer
AWS certifications are developed and created by experts at AWS. This means that these certifications embody best practices for AWS, but also cloud computing in general.
Similar offerings from Microsoft, IBM, and Google are product-specific but serve as a validation of general cloud computing skills. On top of this, companies like Cisco, which has dominated enterprise-level internet and networking, also offer cloud computing certifications however, you can also view our list of free and paid cloud computing training resources to sharpen your skills.
In terms of industry, cloud computing is a good career and has grown in strength over the last few years. The technology is advancing the capability of cloud computing, and large firms are investing heavily to develop into a one-stop shop for all cloud needs.
There is still so much potential, and projected growth rates show that the industry has many expansion opportunities.
The benefits a premium cloud service offers businesses mean as more organizations make their business entirely run through the cloud, specialized engineers will be needed more than ever.