In today’s data-driven world, the ability to visualize complex datasets effectively can be the key to unlocking actionable insights for businesses. With a lot of options available, choosing the right data visualization tool can be a daunting task, especially when considering open source data visualization tools.
These tools offer a cost-effective, flexible solution for businesses looking to explore and present their data in intuitive and impactful ways by giving you options to consider when selecting an open source data visualization tool, ensuring that you can make informed decisions that align with your data analysis needs and goals.
Data visualization tools allow users to explore complex datasets visually so a business can gain actionable insights from the data. They provide an intuitive interface for analyzing data and presenting results.
There are several types of data visualization tools available online. Some are free, whereas others cost money. Free tools may offer limited functionality, whereas paid ones often include additional features.
Data Visualization Tool Features
Free data visualization tools are usually basic and lack advanced features. Paid tools tend to be more robust and feature rich. Most offer a free trial period so you can try them out before making the investment.
It’s best to have a list of features that are pertinent to perform the types of data visualization that you need. Some features will be part of a suite of tools or some may be stand-alone.
Key factors when evaluating open source data visualization tools:
| Customizable charts | Support for multiple file formats | Ability to save images directly to disks | Ability to filter data |
| Interactive graphs | Integration with databases | Ability to change chart titles | Ability to sort data |
| 3D visualizations | Ability to import data from Excel file | Ability to add custom text labels | Ability to group data |
| Ability to export to PDF | Ability to customize color schemes | Ability to rotate | Ability to link to external websites |
| Ability to highlight specific values | Ability to add annotations | Ability to zoom in/out | Ability to embed interactive widgets |
| Ability to generate reports | Ability to access third party libraries | Ability to pan | Ability to share data via email |
| Ability to connect to APIs | Ability to visualize big data sets | Ability to perform regression analysis | Ability to publish data to web pages |
| Ability to run offline | Ability to perform exploratory analysis | Ability to calculate correlations between variables | Ability to integrate with database systems |
| Ability to analyze data using statistical algorithms | Ability to perform predictive analytics | Ability to perform clustering analysis | Ability to apply machine learning techniques |
| Ability to perform factor analysis | Ability to conduct network analysis | Ability to visualize networks | Ability to perform k-means clustering |
| Ability to perform hierarchical clustering | Ability for users to collaborate on projects | Ability to view data over time | Ability to interactively browse data |
| Ability to view live data streams | Ability to store large amounts of data | Ability to store data locally | Ability to scale easily |
|
Ability to handle very large amounts of data |
Ability to support mobile devices | Ability to display real-time data |
Flexible Data Visualizations
Make sure your open source data visualization tools are flexible enough to create all kinds of data displays required for your data management. Your data tool needs to be responsive and adaptable enough to create all kinds of representations needed for your data analysis.
User Experience
User experience refers to how well a user interacts with a system. This includes ease of navigation, speed of interaction, and overall satisfaction.A poor user experience can lead to frustration, dissatisfaction, and abandonment.
When selecting a data visualization tool, you should evaluate its user experience especially if there are going to be other business users using the system.
For example:
- Does it seem too complicated to navigate? Data visualization software should be easy for users to navigate through large amounts of information. Users should not need to spend hours searching for specific pieces of information or trying to figure out how to use the software.
- Does it take too much time to learn how to use it? It should have easy instructions and videos on how to create at least the popular bar charts, pie charts, 3D charts, bar graphs, scatter plots, interactive visualizations, static visualizations, and others to help you gain deeper insight into your data.
- Is there a steep learning curve? If new to using dataviz tools, making sense of massive amounts of data can be a large task, so make sure the tool has a wide array of options to fully learn how to accomplish the visuals and graphics you need easily.
- Does it feel slow? It’s important that can manipulate and handle the amount of data you are working with. If it lags with what you input, then try another tool.
- Are there any bugs and errors? Make sure the software is consistently being updated to clear out bugs and error messages to keep it working for the users and that there is access to help features.
- Is it difficult to understand what each button means? Each tool should have self-help features or easily identifiable buttons so you can navigate easily throughout the program.
- Are there any missing features? Make sure you are able to download or display all the business intelligence you need from the software.
- Can you easily share the data visualization? The ability to share data visualization online is becoming increasingly important. Many companies now publish their data online, allowing anyone with access to the internet to view and analyze the data.
Pricing Structure
Pricing structure refers to whether you pay per month, annually, or upfront.
Many free data visualization tools are ad supported. Most paid tools typically charge monthly fees.
This type of pricing model makes sense for smaller businesses that don’t plan to use the service frequently.
However, these services do not provide sufficient value to justify paying monthly fees.
Other free open source data visualization tools are freemium models. For example, Google Sheets provides a free version that allows users to create simple tables and charts. However, they require payment to unlock additional features such as creating dashboards, exporting data into Microsoft Office products, saving data to Google Drive, and sharing data with colleagues.
These services are useful for small business owners who want to quickly create simple reports without spending money.
Most paid data visualization tools are subscription based. Subscription plans range from $10-$100+ per month depending on the number of users.
Subscriptions are ideal for larger companies that need to regularly update their data visualization needs.
They also make sense for organizations that need to share data with many people.
Security
It’s important to verify the security features of your data visualization tool. Hackers attempt to compromise computers and steal sensitive information meaning your valuable data.
To protect against security threats, most data visualization tools encrypt data before sending it to remote servers. Encryption scrambles data so that it cannot be read by anyone else. This data is sent securely to remote servers where it is decrypted and analyzed.
If there are several people accessing your data on the web, security should be a top priority.
FAQ About Choosing a Data Visualization Tool:
Does data visualization require coding?
Many open source data visualization tools require coding, but not necessarily any kind of programming. There are many ways to visualize data without writing code.
Some of these methods include creating charts, graphs, maps, and diagrams. These visualizations are created using tools like Tableau, Excel, PowerPoint, Visio, and others. However, if you’d prefer to write code, there are plenty of options available. Many of these programs are free, such as R, Python, and Matlab. Others cost money, such as Java, C++, and PHP.
Regardless of which language you choose, learning how to program is a great skill to have. Whether you’re working alone or collaborating with others, having the ability to write code will give you a competitive edge.
How do you choose which kind of visualization to use?
Data visualization tools are used to create visual representations of large amounts of information. They’re often used to communicate complex ideas, summarize statistics, or highlight important patterns within data.
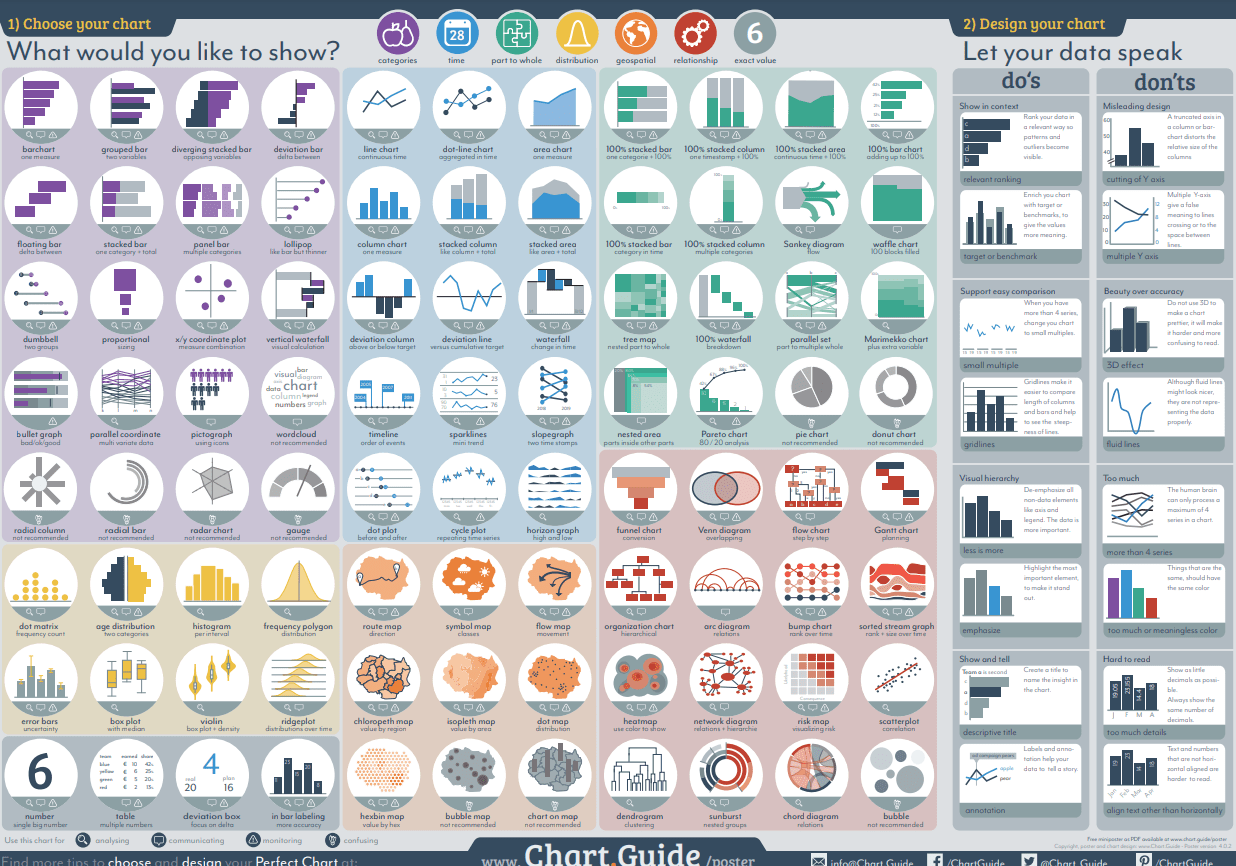
There are many different types of data visualization tools available, including bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, scatter plots, maps, and timelines. Each type of chart has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to understand them well before deciding which one to use.
When choosing a data visualization tool, consider these factors:
- What kind of data am I trying to visualize? Bar charts work well when there are discrete categories of data, such as gender, age, income, etc., whereas pie charts are better suited to continuous variables, such as sales volume, number of employees, etc.
- Do I need to show multiple dimensions? Line graphs are great for showing two or three variables at once, but they can be hard to interpret when there are four or five variables. Maps are useful for showing geographic locations, but not very effective for displaying data points.
- Is this a static presentation or interactive? Static presentations are usually easier to design because they require fewer elements than interactive ones. However, they may lack interactivity and flexibility, making them harder to update. Interactive presentations allow users to manipulate data through various controls, such as sliders, buttons, and dropdowns. This makes them ideal for presenting dynamic data, such as stock prices, weather forecasts, and real-time events.
What is web-based data visualization?
Web-based data visualization is data represented via the web to include interactive maps, charts, graphs, and tables.
Web-based data visualization is becoming increasingly popular among businesses because it provides a cost-effective method of communicating complex ideas and concepts to large audiences. It’s also a great way to attract attention and interest from consumers.
For example, the infographic by the National Geographic Society shows the world’s top 10 cities according to population density, and it includes a map showing the location of each city. Another example of web-based visualization is the interactive map created by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. The USDA uses this map to track food safety issues, such as recalls and outbreaks.
Both of these examples demonstrate how web-based data visualization can be used to communicate complicated topics in ways that are easy to understand.